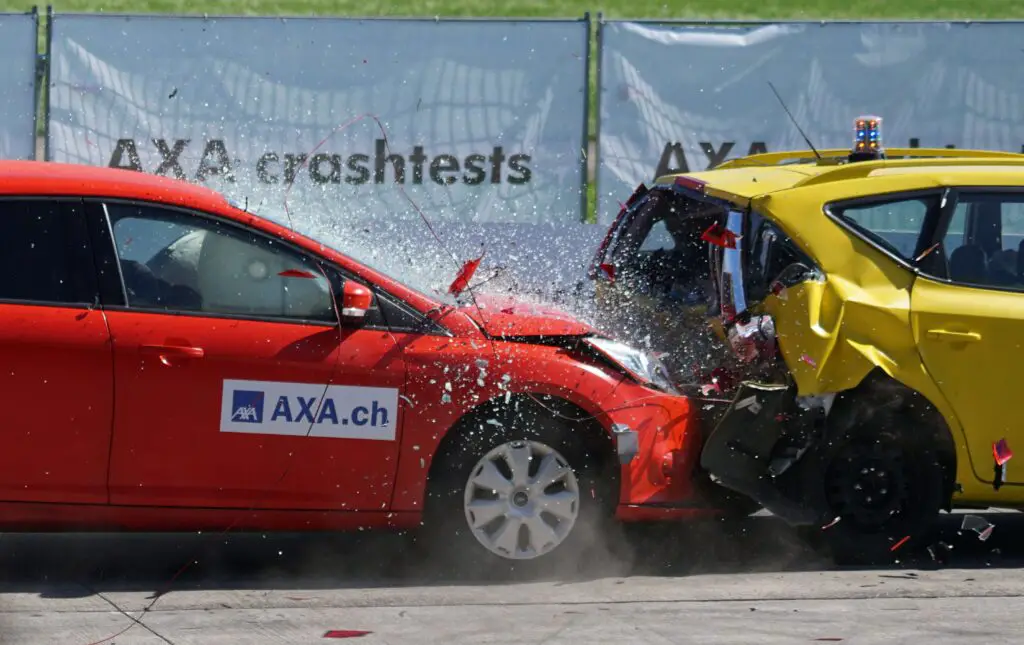
When it comes to car accidents involving children, it is essential to understand the concept of parental liability. As a parent, it is important to be aware of your legal responsibilities and the potential consequences if your child is involved in a car accident. This article will delve into the legal principles surrounding parental liability, the factors that determine it, and the defenses that can be used against it.
Are parents liable for children’s car accidents?
Parents can be held liable for their children’s car accidents under certain circumstances. The legal doctrine of parental liability holds parents responsible for the actions and behavior of their minor children. While the specifics vary from jurisdiction to jurisdiction, the general principle is that parents have a duty to supervise and control their children, including their use of motor vehicles.
Legal principles of parental liability
Parental liability is based on legal principles such as negligence and vicarious liability. Negligence refers to the failure to exercise reasonable care, resulting in harm to others. In the context of children’s car accidents, negligence may involve a parent’s failure to properly instruct and supervise their child or allowing them to drive without a license or in an unsafe manner.
Vicarious liability, on the other hand, holds parents responsible for the actions of their children due to the parent-child relationship. This means that even if a parent did not directly cause the accident or participate in the negligent conduct, they may still be held liable for their child’s actions.
Read About: Does a Guardian ad litem Choose Parent with Better Job
Age limits and parental responsibility
The age at which a child can be held responsible for their actions varies from jurisdiction to jurisdiction. In some places, there is a specific age, such as 16 or 18, at which a child is considered responsible for their own negligence. However, in many cases, parental liability can extend beyond these age limits if it can be shown that the parent was negligent in their supervision or control of the child.
Understanding negligence in children’s car accidents
To establish parental liability in a child’s car accident, it is necessary to prove negligence on the part of the parent. Negligence can be demonstrated by showing that the parent failed to meet the standard of care expected of a reasonable parent in similar circumstances. This may include failing to provide proper instruction, allowing the child to drive without a license, or permitting them to operate a vehicle that is not roadworthy.
It is important to note that the standard of care may vary depending on the age and experience of the child. Younger children may require closer supervision and stricter controls, while older teenagers may be expected to demonstrate more independence and responsibility.
Factors that determine parental liability
Several factors are considered when determining parental liability in children’s car accidents. These factors may include the age and maturity of the child, whether the child was acting within the scope of their permitted use of the vehicle, and whether the parent knew or should have known of the child’s propensity for reckless driving. Additionally, the court may consider whether the parent provided adequate instruction and supervision, as well as whether any laws or regulations were violated.
Consequences of parental liability
The consequences of parental liability can be significant. Parents may be held financially responsible for the damages caused by their child’s car accident, including medical expenses, property damage, and compensation for pain and suffering. In more serious cases, parents may also face criminal charges or other legal penalties.
Moreover, parental liability can have long-term consequences for a parent’s insurance rates and driving record. Insurance companies may view parents of children involved in accidents as higher-risk drivers, resulting in increased premiums or even policy cancellations.
Defenses against parental liability
There are several defenses that can be used against parental liability in children’s car accidents. One defense is the “sudden emergency” doctrine, which applies when a parent is faced with an unforeseen and sudden event that leaves them with little time to react or prevent the accident. Another defense is the “independent contractor” theory, which suggests that the child was acting as an independent driver rather than under the control and supervision of the parent.
Additionally, it may be possible to argue that the child’s actions were not reasonably foreseeable or that the parent took reasonable steps to prevent the accident, such as providing proper instruction and supervision.
Insurance coverage for parental liability
Parents should review their insurance policies to determine whether they have coverage for parental liability. Some auto insurance policies may provide coverage for accidents caused by family members, including minor children. However, the extent of coverage and any limitations or exclusions should be carefully examined. It may be necessary to purchase additional coverage or consider umbrella insurance policies to ensure adequate protection.
How to protect yourself from parental liability
To protect yourself from parental liability in children’s car accidents, there are several steps you can take. First and foremost, ensure that your child is properly trained and licensed before allowing them to operate a motor vehicle. Teach them about the importance of safe driving practices and set clear rules and expectations.
It is also important to lead by example and be a responsible driver yourself. Avoid engaging in reckless or negligent behavior behind the wheel, as it can influence your child’s attitudes and actions. Regularly communicate with your child about safe driving practices and reinforce the importance of obeying traffic laws.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding parental liability in children’s car accidents is crucial for parents. By being aware of your legal responsibilities and the potential consequences, you can take proactive steps to protect yourself and your family. Remember to provide proper instruction and supervision, ensure your child is licensed and follows the rules of the road, and review your insurance coverage to mitigate the financial risks associated with parental liability. By doing so, you can help ensure the safety of your child and others on the road while minimizing your legal exposure.